DNA/RNA Dynamics by Field-Cycling NMR
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) is a molecule that makes make critical functions in biological systems. Especially now during COVID-19 pandemics, RNA virus related investigations are urgent and important topics. Therefore, the studies of how RNAs function in virus transportation between cells and its collaborated proteins now become the highlight of current biological chemistry studies. NMR has a great insight into understanding conformations and dynamics. NMR COVID-19 project organizes all related NMR studies of COVID-19 RNA and protein and provides a global transparent platform for researchers.
Despite RNA structures, dynamics and molecular interactions are also crucial but rarely studied compared with structural investigations.
NMR is a practical tool for investigation motions by probing its 31P, 13C, and 15N. An early example of nuclear dynamics by field-cycling NMR is the dynamics of DNA octamers probed by field-dependent longitudinal relaxation curves, which are probed by 31P. Since field-dependent relaxation study can probe molecular motions from microsecond to picosecond timescales, it can also become a practical manner of RNA dynamics investigation. Combining other NMR methods, such as EXSY, one can even discover many RNA excited states and attempts to investigate correlated functions for having a more complete understanding of RNA functions.
Here, we listed a review of RNA dynamics by NMR spectroscopy and an example of DNA dynamics studied by field-cycling NMR in this issue. This example of field-cycling NMR had conducted a pneumatical driving system to reach the aim of field-cycling during measurement. Nowadays, field-cycling manner has a more precise control on the sample shuttling. Increasing the precision and resolution of field-cycling studies benefits studying more complicated systems, such as RNA. Detailed information can be seen here .
Related Literature
RNA Dynamics by NMR spectroscopy
M. Marušič, J. Schlagnitweit, K. Petzold, ChemBioChem 2019, 20, 2685.
An ever‐increasing number of functional RNAs require a mechanistic understanding. RNA function relies on changes in its structure, so‐called dynamics. To reveal dynamic processes and higher energy structures, new NMR methods have been developed to elucidate these dynamics in RNA with atomic resolution. In this Review, we provide an introduction to dynamics novices and an overview of methods that access most dynamic timescales, from picoseconds to hours. Examples are provided as well as insight into theory, data acquisition and analysis for these different methods. Using this broad spectrum of methodology, unprecedented detail and invisible structures have been obtained and are reviewed here. RNA, though often more complicated and therefore neglected, also provides a great system to study structural changes, as these RNA structural changes are more easily defined—Lego like—than in proteins, hence the numerous revelations of RNA excited states.
High-Resolution Field-Cycling NMR Studies of a DNA Octamer as a Probe of Phosphodiester Dynamics and Comparison with Computer Simulation
Mary F. Roberts, Qizhi Cui, Christopher J. Turner, David A. Case, and Alfred G. Redfield Biochemistry 2004 43 (12), 3637-3650
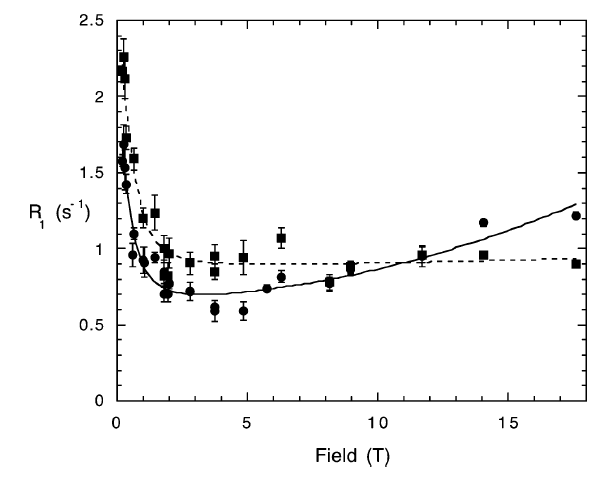
Phosphorus-spin longitudinal relaxation rates of the DNA duplex octamer [d(GGAATTCC)]2 have been measured from 0.1 to 17.6 T by means of conventional and new field-cycling NMR methods. The high-resolution field-cycling method is identical to a conventional relaxation experiment, except that after preparation the sample is moved pneumatically from its usual position at the center of the high-resolution magnet upward to a lower field above its normal position and then returned to the center for readout after it has relaxed for the programmed relaxation delay at the low field. This is the first measurement of all longitudinal relaxation rates R1 of a nuclear species in a macromolecule over virtually the entire accessible magnetic field range....
